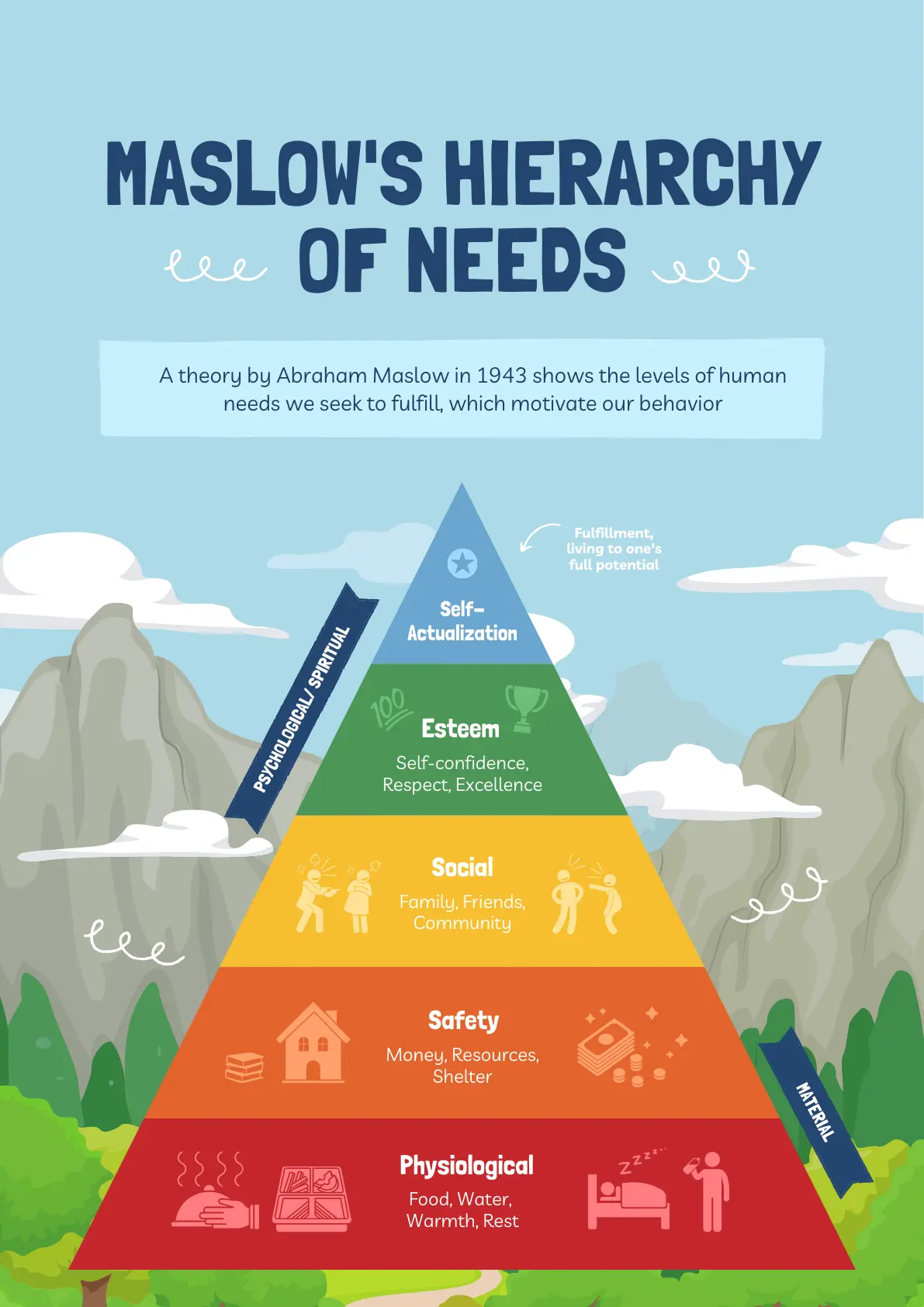
A Guide to Maslow s Theory of Motivation
In 1943, Abraham Maslow published a paper titled "A Theory of Human
Motivation," which introduced his now-famous Hierarchy of Needs. This
pyramid-shaped model proposes that human needs are arranged in a hierarchy,
with the most basic needs at the bottom and the most complex needs at the top.
According to Maslow, people are motivated to fulfill basic needs before moving
on to other, more advanced needs.
Needs lower down in the hierarchy must be satisfied before individuals can
attend to needs higher up. From the bottom of the hierarchy upwards, the needs
are: physiological, safety, love and belonging, esteem and self-actualization.
Physiological Needs
The most basic needs are physiological needs, which are necessary for
survival. These include the need for food, water, air, shelter, sleep, and
sex. If these needs are not met, it is difficult to focus on anything else.
For example, if you are hungry, it is difficult to concentrate on work or
school. The physiological needs include those that are vital to survival. Some
examples of physiological needs include:
- Food
- Water
- Breathing
- Homeostasis
In addition to the basic requirements of nutrition, air, and temperature
regulation, physiological needs also include shelter and clothing. Maslow
included sexual reproduction in this level of the hierarchy as well, since it
is essential to the survival and propagation of the species.
Safety Needs
Once physiological needs are met, people turn their attention to safety needs.
These include the need for physical safety, security, and stability. Safety
needs are often triggered by fear or anxiety. For example, if you live in a
dangerous neighborhood, you may be more concerned with safety than with
self-actualization. At the second level of Maslow’s hierarchy, the needs start
to become a bit more complex. At this level, the needs for security and safety
become primary.
People want control and order in their lives. Some of the basic security and
safety needs include:
- Financial security
- Health and wellness
- Safety against accidents and injury
Finding a job, obtaining health insurance and health care, contributing money
to a savings account, and moving to a safer neighborhood are all examples of
actions motivated by security and safety needs.
Love and Belonging Needs
After safety needs are met, people turn their attention to love and belonging
needs. These include the need for love, affection, intimacy, and belonging.
Love and belonging needs are important for mental health and well-being. For
example, if you do not have close relationships, you may feel lonely and
isolated. The social needs in Maslow’s hierarchy include love, acceptance, and
belonging. At this level, the need for emotional relationships drives human
behavior. Some of the things that satisfy this need include:
- Friendships
- Romantic attachments
- Family relationships
- Social groups
- Community groups
- Churches and religious organizations
In order to avoid loneliness,
depression, and
anxiety, it is important for people to feel loved and accepted by others. Personal
relationships with friends, family, and lovers play an important role, as does
involvement in groups—such as religious groups, sports teams, book clubs, and
other group activities.
Esteem Needs
Once love and belonging needs are met, people turn their attention to esteem
needs. These include the need for
self-esteem, confidence, achievement, and respect from others. Esteem needs are
important for self-worth and motivation. For example, if you do not feel
confident in your abilities, you may be less likely to take risks or pursue
your goals. At the fourth level in Maslow’s hierarchy is the need for
appreciation and respect. Once the needs at the bottom three levels have been
satisfied, the esteem needs begin to play a more prominent role in motivating
behavior.
At this level, it becomes increasingly important to gain the respect and
appreciation of others. People have a need to accomplish things, then have
their efforts recognized. In addition to the need for feelings of
accomplishment and prestige, esteem needs include such things as self-esteem
and personal worth.
People need to sense that they are valued by others and feel that they are
making a contribution to the world. Participation in professional activities,
academic accomplishments, athletic or team participation, and personal hobbies
can all play a role in fulfilling the esteem needs.
People who are able to satisfy esteem needs by achieving good self-esteem and
the recognition of others tend to feel confident in their abilities.
Conversely, those who lack self-esteem and the respect of others can develop
feelings of inferiority.
Self-Actualization Needs
At the top of the hierarchy are self-actualization needs. These include the
need to fulfill one s potential, to be creative, and to make a difference in
the world. Self-actualization needs are often expressed through work, hobbies,
and relationships. For example, someone who is self-actualized may be a
successful artist, entrepreneur, or scientist. At the very peak of Maslow’s
hierarchy are the self-actualization needs. Self-actualizing people are
self-aware, concerned with personal growth, less concerned with the opinions
of others, and interested in fulfilling their potential.
"What a man can be, he must be," Maslow explained, referring to the need
people have to achieve their full potential as human beings.
Maslow’s said of self-actualization: "It may be loosely described as the full
use and exploitation of talents, capabilities, potentialities, etc. Such
people seem to be fulfilling themselves and to be doing the best that they are
capable of doing. They are people who have developed or are developing to the
full stature of which they capable."
Different Types of Needs
Maslow s hierarchy of needs can be separated into two types of needs:
deficiency needs and growth needs.
Deficiency needs: Physiological, security, social,
and esteem needs are deficiency needs, which arise due to deprivation.
Satisfying these lower-level needs is important to avoid unpleasant feelings
or consequences.
Growth needs: Maslow called the needs at the top of
the pyramid growth needs. These needs don t stem from a lack of something, but
rather from a desire to grow as a person.
While the theory is generally portrayed as a fairly rigid hierarchy, Maslow
noted that the order in which these needs are fulfilled does not always follow
this standard progression.
The Expanded Hierarchy of Needs
In 1970, Maslow built upon his original hierarchy to include three additional
needs at the top of his pyramid, for a total of eight:
Cognitive needs. This centers on knowledge. People generally want to
learn and know things about their world and their places in it.
Aesthetic needs. This addresses the appreciation of beauty and form.
People might fulfill this need through enjoying or creating music, art,
literature, and other creative expressions.
Transcendence needs. Maslow believed that humans are
driven to look beyond the physical self in search of meaning. Helping others,
practicing spirituality, and connecting with nature are a few ways we might
meet this need.
Implications for Daily Lifestyle
Pyramids are a common way to represent Maslow s hierarchy of requirements. The
most fundamental requirements are found at the base of the need pyramid, while
the most complicated demands are found at the summit.
People can proceed to the next level of demands once their lower-level wants
have been satisfied. Psychological and social needs increase as people go up
the pyramid.
The need for self-worth and a sense of achievement is ranked highest on the
pyramid. Similar to Carl Rogers, Maslow placed a strong emphasis on the
concept of self-actualization—the process of evolving personally in order to
realize one s own potential.
Maslow s Hierarchy of Needs has important implications for our daily lives. By
understanding our own needs and the needs of others, we can make choices that
will help us live happier and more fulfilling lives.
Here are a few examples of how Maslow s Hierarchy of Needs can be applied to
daily life:
-
Eat a healthy
Diet
and get enough sleep. This will help you meet your
physiological needs for food and sleep.
-
Exercise regularly. This will help you meet your physiological needs for
exercise and can also help you meet your safety needs by reducing stress and
anxiety.
-
Spend time with loved ones. This will help you meet your love and belonging
needs.
-
Set goals and work towards achieving them. This will help you meet your
esteem needs.
-
Find a career that you are passionate about. This will help you meet your
self-actualization needs.
Maslow s Hierarchy of Needs is a valuable tool for understanding human
motivation. By applying this model to our own lives, we can make choices that
will help us achieve happiness and fulfillment.
However, Maslow s Hierarchy of Needs can be a valuable tool for understanding
human motivation and making choices that will help us live happier and more
fulfilling lives.